TUTORIALS
The Circuit making competitions is being organized at SPECTRA.For all those participating in this event this page provides a short tutorials on the topics required to be known.
The list of basic important topics to be known:
- LOGIC GATES
- IC 555
- IC 741
- BASIC OF TRANSISTOR
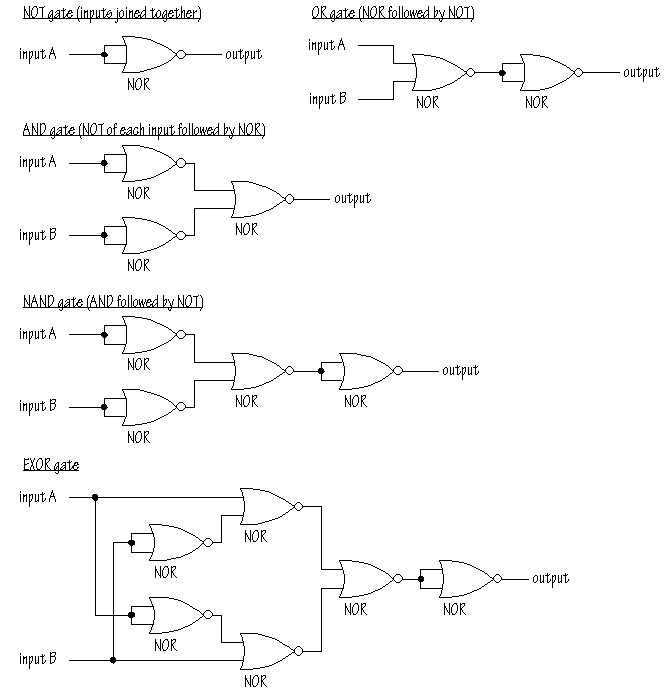
LOGIC GATES:
In this section you should know the truth table and IC numbers of the Basic gates as well Universal Gates(NAND , NOR).Besides this you should also know the XOR and XNOR gates as well as building of all the gates (AND,OR,NOT,XOR,X NOR) using the universal gates(NAND and NOR).
SYMBOL OF BASIC GATES and TRUTH TABLE:
BASIC GATES USING NAND:

BASIC GATES UISNG NOR
IC 555 :
This is the most popular IC and the most used among electronic enthusiast.The IC can operate in two basic modes ASTABLE and MONO STABLE mode.In Monosatble mode the IC gives a Single Pulse after a delay set by the values of R and C while in ASTABLE mode it gives a train pulse whose frequency and on-off time is determined by the value of R and C.
YOU NEED TO KNOW THE PIN-OUT:
555 in ASTABLE MODE:
555 in MONOSTABLE MODE:
IC 741:
This is OP-AMP IC.a OP-AMP is operational amplifier which has a variable gain.the IC can be used in two mode as INVERTING AMPLIFIER and the NON-INVERTING AMPLIFIER.
Transistors:
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems.
Simplified operation
1) Transistor as a switch:
Transistors are commonly used as electronic switches, both for high-power applications such as switched-mode power supplies and for low-power applications such as logic gates.
A switch is a device that is used to 'open' or 'close' a circuit. Opening a circuit means creating a break in the circuit, preventing current flow and thus, turning it 'off'. Closing a circuit, on the other, means completing the circuit path, thereby allowing current to flow around it and thus, turning it 'on'. When the switch is closed, the transistor goes into saturation, due to which the voltage at the output is zero. When the switch is open, the transistor goes into Cut-off State, as there is no base current. Hence the collector current drops to zero. Now, as there is no current flowing through resistor, the collector voltage rises to the supply voltage (5V) and voltage at the output is 5V.
2) Transistor as an amplifier:
The transistor can be used as a Amplifier in various configurations having different gains hand input impedance as well different advantages and dis advantages.The three basic configuration in which it is used as a amplifier is Common Emitter(CE) Common collector(CC) and Common Base(CB)